Part 2 – What are effects of Type-2 Diabetes
and How to measure levels of Diabetes
AffordableMeds.org
March 22, 2021
In Part-1 of this series covered what Type-2 diabetes is.
Diabetes is a chronic diseases and if not
controlled properly, adverse effects of this disease could be severe. Example of such effects are given below.
Risk of Stroke
Loss of Consciousness
Extreme Thirst
Visual Disturbance (could lead to blindness -
Sweet smelling breadth
Risk of heart disease
High blood pressure
Gastroparesis (Delayed emptying of food from stomach)
Fatigue and lack of energy
Pancreas Malfunction
Excessive Urination
Ketoacidois (Ketones which
are toxic acids in body)
Protein in the urine (Damaged in kidney)
Dry and cracked skin
Damaged Blood Vessels
Nerve damage
Foot problems.
In Part-3 of this series, we will discuss what
medications, diets and exercise can help control the disease.
In this part (Part-2), we focus on how does one measure the severity of diabetes.
Glucose in blood is measured and reported as milligrams per
deciliter. A milligram (mg) is one-thousandth of a gram and a deciliter (dL) is metric unit of capacity equal to one tenth of a
liter.
The normal
value of blood
sugar for a person
without diabetes is 70–99 mg/dl measured
after fasting and normal blood sugar 2 hours after meals less than 140 mg/dl.
When a
person’s bloodsugar
level is above the normal, the person is considered diabetes.Whether the diabetes
is type-1 or type-2 shall be decided whether that pancreas is producing enough
insulin or not.
The normal range of blood sugar level is 70-99 mg/dl. Blood sugar level above 99 mg/dL is hyperglycemia (diabetes) and below 70
mg/dL is hypoglycemia.
When glucose (sugar) enters the blood, it binds to the
protein in the red blood cells. This binding creates “glycated
hemoglobin”. The more sugar in the blood, the more glycated
hemoglobin the
A1C test measures the percentage of your red blood cells that have sugar-coated
hemoglobin. The A1c is
an average of what your blood sugar levels have been over the last 3-month
period (average life of a red cell is 3 months). In general, the higher your
A1C number, the higher your likelihood of diabetes complications. Higher A1C means
there is too much sugar in your blood and your body isn’t absorbing it.
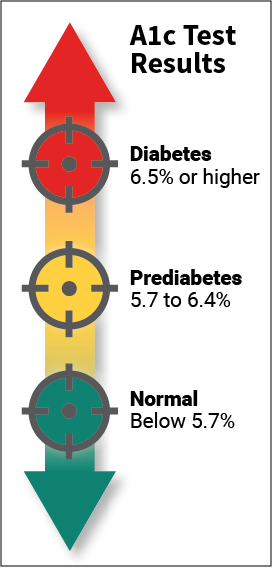
HbA1c
Normal for person without diabetes: Less than 5.7%
Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes: Less than 7.0%
A1C NUMBER = HOW MUCH SUGAR IN THE BLOOD?
|
A1C
level
|
Estimated
average blood sugar level
|
|
5 percent
|
97 mg/dL (5.4 mmol/L)
|
|
6 percent
|
126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L)
|
|
7 percent
|
154 mg/dL (8.5 mmol/L)
|
|
8 percent
|
183 mg/dL (10.2 mmol/L)
|
|
9 percent
|
212 mg/dL (11.8 mmol/L)
|
|
10 percent
|
240 mg/dL (13.3 mmol/L)
|
|
11 percent
|
269 mg/dL (14.9 mmol/L)
|
|
12 percent
|
298 mg/dL (16.5 mmol/L)
|
|
13 percent
|
326 mg/dL (18.1 mmol/L)
|
|
14 percent
|
355 mg/dL (19.7 mmol/L)
|